We use the ungrounded electrical system in many places. We will discuss in this post, what is ungrounded electrical system, the differences from a grounded system, its advantages and disadvantages, and its applications.
What is an ungrounded electrical system?
The ungrounded electrical system is an electrical system without grounding (earthing) at any point of the system. It is also called a floating electrical system or electric system without earthing.
Figure 1 shows an ungrounded electrical system without any earth connection.
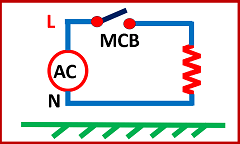
Note that the neutral wire of the system is floating and has no connection with the earth or ground. In the case of a normal system neutral is connected to the earth or ground.
We also call it an insulated neutral earth system or floating electrical system.
Reason (advantages) for using an ungrounded electrical system
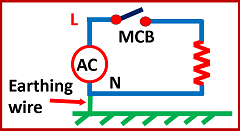
Now refer to Fig 2. Figure 2 shows a grounded electric system. If there is a fault like a line to ground fault, then short circuit electric current flows in the MCB breaker, and the breaker will trip. Now the system will become nonfunctional.
Now refer to Figure 3. Figure 3 shows the ungrounded electrical system. Suppose a fault occurs between the line and the ground. See the ground fault in red color in Figure 3 in an electrical system without earthing.
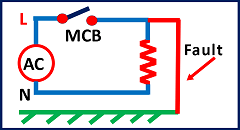
Now even in the case of line-to-ground fault, no short circuit current flows in the MCB circuit breaker, as there is no return path for the short circuit current due to the absence of neutral earthing.
And the system continues to function properly.
However, if another one more neutral to ground fault comes (with 1st fault still present), then MCB will trip, as current may flow between 2 faults.
Difference between grounded and ungrounded electrical system
Fault (First) in the electrical system – advantage of ungrounded electrical system
- In the case of a grounded electric system. short circuit current flows in the MCB. Then MCB will trip, and the system may become unfunctional.
- In the case of a floating electrical system, short circuit current does not flow in MCB. So the MCB does not trip and the system continues to function. However, we need to repair the fault as soon as possible to avoid problems due to the second fault.
2nd fault comes in an electrical system
If 1st fault still exists and the second fault also comes, then:
- In the case of an ungrounded system, MCB will trip and the system may become nonfunctional. And then no equipment will work.
- So, it is essential to repair the first fault up to the extent possible without waiting for the second fault to appear in the case of the ungrounded system.
Disadvantage of ungrounded electrical system
The main disadvantage of an ungrounded electrical system is safety problems for humans.
However, this kind of system always works in a protected area. And nobody is allowed near the electrical system.
Further, an ungrounded electrical system may have more noise problems compared to an earthed electrical system.
Applications of ungrounded electrical system
We need an ungrounded electrical system for the continuous functional requirements. Some of the ungrounded system examples are ( as per necessity):
- Ships
- Train engine
- Chemical industries
- Telecommunication
It is also used in CRO or DSO power supply for technical reasons.
Extra knowledge as per experience
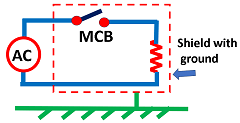
Shield for protection
We can provide a shield to protect from ungrounded systems. The circuit is enclosed in an enclosure and then the enclosure is connected to the ground as per Figure 4.
Conversion of grounded system to ungrounded system
We can convert a grounded electrical system into an ungrounded electrical system by using an isolation transformer.
The transformer secondary will not be connected to the ground.
The same method we use to make ungrounded AC supply for DSO scope. This helps in solving measuring problems.
An ungrounded system is used for low-voltage applications. Using an ungrounded electrical system at high voltage may create too much safety, generation of very high voltage and noise problems for equipment.
Grounding does not mean that equipment should be connected directly to the earth. The equipment is connected to a nonfloating electrical system is like a grounding and not a floating equipment.
Do it yourself – solve the problem yourself
We can not connect a flying airplane to the earth. But the electrical equipment located in it, neither has noise, nor high voltage. Just think over, why it is so. Enjoy solving this question yourself.
For more knowledge on this topic, you can watch the video:
I hope that you enjoyed reading the article on the ungrounded electrical system, its advantages and disadvantages, and its applications.
If you like this post then subscribe to my YouTube channel, G K Agrawal
Also, read. use of open circuit CT transformer.
Continue reading AC or DC which is more dangerous.
Further, read the article on what is MOV varistor.
Also read, how do bullet trains move so fast?
Further read, what is tilting electric train
Also read, why stock prices change.
About the author – G K Agrawal B.Sc and B.Tech (from HBTU Kanpur), Retd. Sr DGM Design (BHEL), the inventor of patents, has lifelong industry experience in the electrical and electronics design field of R&D. He worked for BHEL. He shares his experience and knowledge on blogs and YouTube. Read the profile here.


There may be noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain good factors in options also.