The voltage of neutral wire or voltage difference between neutral and earth in AC supply depends on many factors. I will discuss various factors affecting the voltage difference between the neutral and earth in the AC supply.
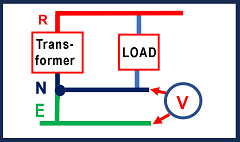
What is the voltage of the neutral wire
The voltage of the neutral wire should be zero in ideal conditions. But there is always some voltage between neutral and earth due to non-ideal conditions.
The voltage difference between neutral and earth will be different at different locations and also vary with time.
Why voltage drop in the neutral wire
The voltage drop in neutral is due to the impedance of the neutral wire. As no wire is ideal in nature.
Refer to figure 1. The neutral wire has some resistance Rn and inductance Ln as per the figure. Even line wire has these resistor and inductor components. But It is not shown here.
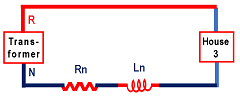
The load current flows in this Rn and Ln, so there will be a voltage drop. This voltage drop is the voltage difference between the neutral wire and the earth.
And this voltage drop will increase with the length of the wire and also with the load current.
Now, the total length of the neutral wire is divided into two parts.
The first part of the neutral wire is the common neutral wire. Which comes from an electrical transformer of electricity board up to the entrance point of electricity in our house or office.
This part of the neutral wire is common, as it is common for all houses.
The second part of the neutral wire is within our house. This is the exclusive neutral wire and is used by us only.
So the voltage of the neutral point in our house will depend on both the voltage drop. One voltage drop is in the common neutral wire. And another voltage drop is in our exclusive neutral wire.
The voltage drop in the neutral wire depends on the current flow in the neutral wire.
The voltage drop in the common neutral wire
The common neutral wire coming into our locality is shared by many houses. And the different houses will have different loads also.
Further different houses share different lengths of the neutral wire. Refer figure 2
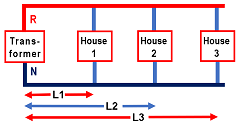
All three houses share different lengths (L1, L2, and L3) of the neutral wire. So voltage drop will be different.
Further, generally, houses use a single-phase supply, but the supply coming from the electricity board is three phases type.
So to create balance, different houses get supply from different phases.
One set of houses will get supply from the R phase and common neutral.
Another set of houses gets supply from the Y phase and common neutral.
And remaining houses get supply from the B phase and common neutral.
So current flowing in common neutral will be a summation of all three currents.
And this current is the vector summation of the current flowing in all three phases.
As these current have 120-degree phase shifts, total vector addition becomes zero.
But practically, these three currents will not be equal as different houses will draw different currents. These currents of different houses will be different in magnitude as well as the type (power factor).
This is called the unbalanced load in the technical term.
This means even if three different house load current is equal. Net total current still will not be zero due to different types of load.
This unbalance current flow in the common neutral wire will create a voltage drop in the neutral wire.
The same thing is applicable to individual houses also. If the supply is 3 phases in a single house then the neutral current will be zero if the load is equal in magnitude and type in all three phases.
But the load is never equal in all three phases in the house. So always some current flows in a neutral wire, both in a common neutral wire and also in an exclusive neutral wire in the house).
The neutral wire in our house
This voltage drop depends on the current flow in the various load in our houses.
As different loads are located at different electrical points with different lengths of the neutral wire. And also load current is different for the different loads.
So voltage drops at different neutral points in different rooms will be different.
If the power supply in the home is a three-phase type, then the current of all the 3 phases will flow in the neutral wire. But this current again will not be zero. So voltage drop will be there in the neutral wire.
Factors deciding voltage of the neutral point
So voltage drop in the neutral wire or voltage difference between neutral and earth will depend on
- The current in the neutral wire, which is different in a different house
- The total current in each phase from all the houses, which is again not equal for all the three phases
- And the length of the neutral wire, which is again different for different house
- The value of the load current will change with time and the load current is not fixed
- The types of the load like the resistive or inductive current
So you can see how difficult it is to tell the voltage at the neutral wire.
It can be measured and may not be possible to calculate.
The voltage of the neutral point is nothing but the voltage difference between neutral and earth in an AC supply.
So voltage difference between neutral and earth
- will be different at different points.
- it changes with time due to changes in the load
I measured the voltage difference between neutral and earth in my house.
The voltage difference between neutral wire and earth in my house is about 5 to 6 volts. Sometimes it goes up to 10 volts. Further, it has different values in different rooms.
Further, if the load in the neighbor’s house is changing then the voltage of neutral in our house will also change. This is due to the common length of neutral wire shared by both houses.
The voltage difference between neutral and earth in the range of a few volts does not create any problem and it is safe. All the electrical equipment is designed for this.
Conclusion
Many factors decide the voltage of neutral wire or, the voltage difference between neutral and earth. The main factors are, the impedance of the neutral wire, length of the neutral wire, unbalance in load, and type of the load. A few volts in neutral wire does not harm the equipment and is acceptable.
Further, read How a current transformer works.
Also, read Why Neutral in Induction motor
Keep learning and read Why neutral earthing of substation transformer?
Also, read How to use open circuit CT transformer?
Further, read Why power factor improvement?
Also, read why the 30 mA RCCB breaker is used.
If so, then subscribe to my YouTube channel.
About the author – G K Agrawal B.Sc and B.Tech (from HBTU Kanpur), Retd. Sr DGM Design (BHEL), the inventor of patents, has lifelong industry experience in the electrical and electronics design field of R&D. He worked for BHEL. He shares his experience and knowledge on blogs and YouTube. Read the profile here.