Nowadays, the problem of electrical fire is increasing. In this post, we will discuss arc fault protection devices, what is AFCI breaker or AFDD breaker and how it works. As this AFCI or AFDD breaker is useful in electrical fire protection.
What is AFCI or AFDD breaker?
AFDD or AFCI breaker protects the electrical system from electrical fire due to the electric arc fault. An arc fault detection device (AFDD) or arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) senses the presence of the arc in the circuit and then disconnects the circuits.
The continued electrical arc produces the heat and burning of components. This results in an electric fire. Fig 1 shows the Siemens make AFDD breaker model 5SM6011-1.

Types of electrical faults
There are three major types of electrical faults in an electrical circuit in homes.
1- Short circuit – MCB breaker protects the circuit from short circuits.
2- Earth leakage current – RCCB breaker protects from earth leakage.
3- ARC fault in the circuit – AFDD or AFCI breaker protects electrical circuits from an arc fault. We are discussing this kind of fault here.
Types of ARC fault
There are three types of arc faults as follow:
1st type – Series arc fault. Refer to fig 2a. If a wire is damaged partially, or insulation is damaged partially. Then arc will take place. As this is a series of loads, so we call it a series arc fault.

2nd type – Line to neutral arc fault (parallel arc fault)– Refer to fig 2b. If there is insulation failure between the line and neutral wire ( 2nd in fig). So arcing will take place.
Note that this is not a full line to neutral short. So MCB will not trip. It is a high impedance type fault. As the fault is in parallel to the load, so we call it a parallel arc fault.
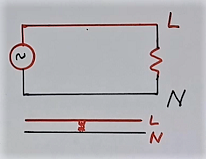
3rd type – Line-to-earth arc fault. This is similar to 2nd type, except that it takes place between the line and the earth.
How arc and electric fire generates in the wire
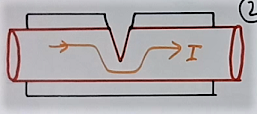
As just one example, refer to fig 3a. An electric current flows in the copper wire. This wire has some insulation like PVC outside.

Now refer to fig 3b. Now suppose there is a partial cut at one side in the copper wire. The same current will continue to flow. But, now current flows through a small area of copper conductor.
As of now, the current density becomes more at the point of fault. So more heating will take place at the point of the cut fault. So temperature will increase at this point. Then the temperature may be very high at this point.
And finally, the small leftover metal portion will melt due to very high temperature. There will be a clear gap now. But current will still flow from this gap due to ionization of the gas in between ( refer to fig 3c.).
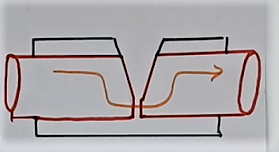
Now refer to fig 3d. Due to heating temperature will become very high. So high temperatures will burn the insulation. And the flame will generate. This flame will further spread as an electrical fire.
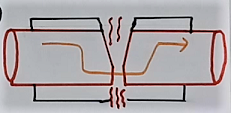
The flame generation will not take place if we trip the electrical system in time with AFCI or AFDD breaker.
Causes of the arc fault
The following are the causes of the arc fault need protection using AFCI or AFDD breaker in an electrical circuit
- Damage of insulation due to nails etc
- Cable breaking due to bending of the wire
- Cable damage due to UV radiation (Outdoor)
- Rodden by rats
- Loose connections
- Deteriorating insulation with time and use
Functional block diagram of the AFCI or AFDD breaker
Fig 4 shows the block diagram of the AFDD or AFCI breaker. Every block indicated inside the dotted line is part of the breaker. It has two incoming wires ( line and neutral) and two outgoing wires for the load.
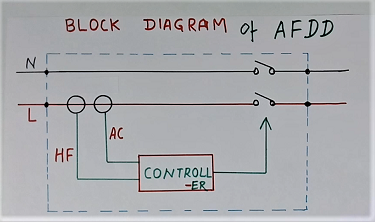
As in the above diagram, It has two current sensors inside the device. One sensor (HF) is for sensing high-frequency current. And 2nd sensor (AC) is to sense low-frequency 50 Hz or 60 Hz current. Arc generates a high-frequency current.
These two current signal goes to the controller. Then controller processes the signals. It also generates the necessary command to open the breaker as required.
Tripping of the AFCI or AFDD breaker should take place only for real arc fault currents. It should not trip due to high-frequency current because of the following:
- Inrush current of fluorescent lamp
- Power drill
- Light dimmer
- Harmonics in power supply
- Other radio frequencies
- Switches
- Motors
The controller algorithm can distinguish arc current from other currents as follows
How sensor differentiates between ARC current and other HF currents in the AFCI breaker
The controller in the AFDD breaker measures the following parameters to differentiate between an arc and a normal high-frequency (HF) current
- Power of the high-frequency current
- HF’s current duration and repetition
- HF current stability
- RMS of normal current
- Synchronization
- Irregularity of the arc
Then controller of the AFCI or AFDD breaker also measures and calculates RSSI, dRSSI/dt, di/dt parameters
{RSSI means Received signal strength indication – the power of the ARC at a defined frequency and bandwidth.}
Then it analyses the waveform ( signature) of the arc current. ( The waveform of different types of HF current may be different. This exclusive waveform is called the signature).
Arc current has its own nature of waveform ( signature)
Waveform or signature of arc fault current
Refer to fig 5 to understand further about AFCI or AFDD breaker. The top waveform shows the total AC current. It has occasionally high-frequency components just before every cycle.
Further, the bottom waveform of fig 5 shows the high-frequency components ( expanded waveform is shown) of the total current. This is the signature of the arc fault current. This signature will be different for different kinds of HF current.
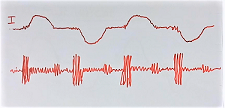
Subsequently, the controller of the AFCI AFDD breaker analysis the above signature current. Refer fig 6
- Waveform “I” is the total current
- Then controller calculates the RSSI (High-frequency power)
- Then controller calculates the dRSSI/dt ( 3rd in fig 6. It is shown as an inverted signal)
- This value is measured and integrated with time. AFCI breaker trips if this value is more than the set value.

Further discussion on AFCI or AFDD breaker
Different countries have different rules. It is compulsory to use AFDD breakers in a few countries. In Some other countries, AFDD should protect the electrical circuit in high-fire-risk areas. Many countries have no rules for this. And the use of this breaker is optional.
Summary
AFDD or AFCI breaker protects the electrical system from electrical fire due to arc fault. The breaker measures the signature of the arc fault current with an algorithm and trips and disconnects the connection if required.
For further learning, watch the below video link. This video explains in detail the function of the breaker.
Further Also read, what are the relays
Also, read Which motor is used in the locomotive
Read more about the Neutral earth difference in Hindi.
Further, read the Differences between MCB breaker and fuse.
I hope you enjoyed reading this post on what is AFCI or AFDD breaker?.
If you like this post then subscribe to my YouTube channel, G K Agrawal
About the author – G K Agrawal B.Sc and B.Tech (from HBTU Kanpur), Retd. Sr DGM Design (BHEL), the inventor of patents, has lifelong industry experience in the electrical and electronics design field of R&D. He worked for BHEL. He shares his experience and knowledge on blogs and YouTube. Read the profile here.



Super explanation and exclusive information.
Hello. Thank you for always good blog강남 가라오케
Hello. Thank you for always good blog강남 셔츠룸
Hello. Thank you for always good blog길동노래방
Hello. Thank you for always good blog강남 가라오케
Hello. Thank you for always good blog강남 셔츠룸
you’re in point of fact a excellent webmaster. The website loading velocity is amazing.
It sort of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick.
Also, The contents are masterwork. you’ve done a fantastic task in this matter!