The 30 mA residual current type RCCB circuit breaker is used in the home. Do you want to know, why a 30 mA RCCB breaker is used at home and is of 30 mA trip rating type and 30 mA RCCB tripping time? And if the use of the 30 mA RCCB breaker is not possible, then what to do?
Then how to use a 300 mA type RCCB breaker? And where to use a higher trip current rating type RCCB breaker.
If you want to know the above, this article is for you.
In this post, I will explain, that why a 30 mA residual current type RCCB breaker is used in the home.
And if 30 mA is not possible. Then how to use a 300 mA residual current RCCB breaker, but still with protection to the human body. And where to use a higher rating type RCCB breaker.

The table of contents of this article is as follows
Why a 30 mA type RCCB breaker is used at home
The 30 mA type RCCB is used at home, as it can disconnect the electrical circuits in 300 ms for a residual current flow of 30 mA. And this current of 30 mA for 300 ms is safe for the human body.
The rating of the RCCB breaker
There are two basic important current ratings of any RCCB breaker.
1- Residual current or tripping current of RCCB
This current is written as I∆n. This is nothing but the residual current setting for RCCB, and it is responsible for tripping the RCCB. So we call it trip current also.
This is current, which flows through the earth from the human body or from electrical equipment. This current can be 30 mA or 100 mA or 300 mA as per requirement.
A 30 mA trip current type RCCB breaker will trip in 300 ms if 30 mA residual current flows through the human body and the earth.
2- Rated current of RCCB (current in contacts)
This current is written as In. This is current, which can flow in the contacts of the RCCB breaker. This is also the same current, which flows in the load connected to the RCCB.
This rated current (In) can be 16 Amps. 25 Amps, 32 Amps, 40 Amps, or 63 amperes as per load requirements.
Whenever we select a breaker, then we must select one current rating from both the above two ratings.
For example, we can select 30 mA from the trip current rating and 32 amperes current from the rated contact current rating.
So, the selected RCCB rating will be 30 mA residual current or trip current and 32 amperes rated current.
In this post, we will discuss the residual or trip current rating of the RCCB breaker.
Before we start, please note that the current flow in the body through the earth, or leakage current from equipment, is the same as the residual currents in the RCCB.
Safe current through the human body and 30 mA RCCB tripping time
The residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) is used to protect the human body from electrical currents. It also protects the equipment in case of leakage current to the earth.
So to decide the trip current of the RCCB, we must know the value of the safe current flow possible in the body.
(Note: I will tell 3 different values of currents in Figures 2, 3, and 4. But in the end, I will tell the difference between them with an example to make it more clear.
Current vs time for RCCB
Figure 2 shows the correlation between safe current in the body vs time. The vertical scale shows the current flow in the body. The horizontal scale shows the time duration for which the current can flow in the body safely.
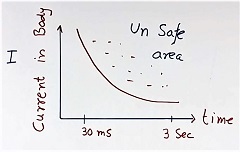
Any point above this plot is unsafe for the human body. The small current can flow for a longer duration in the body safely. The higher current can flow only for the lesser time in the body safely.
We provide residual current circuit breakers (RCCB) for human safety. And the risk level depends upon the current and also on the time duration of the current flow.
So the residual current (or leakage current) and time duration of the residual current flow, both decide the trip command of RCCB.
The RCCB must trip at a lower current than the safe current vs time limit for the body to protect us.
Figure 3 shows the correlation between the trip (residual current in the RCCB) current vs the must-trip time needed for human safety. This plot is as per various standards like IS standard or IEC standard.
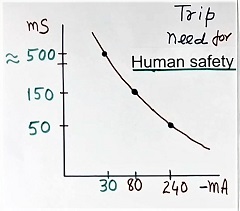
Further, refer to figure 3a. It shows the data as per figure 3 but in a chart, to understand it better.
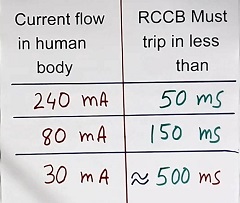
If 240 mA residual current flows in the RCCB (to protect the human body) then RCCB must trip in 50 mSec.
For a residual current of 80 mA, the RCCB breaker should trip in 150 mS.
Further, If a 30 mA residual current flows in the RCCB, the RCCB must trip in about 500 mS (approximately taken).
Actual RCCB tripping time
Above, I explained the must-trip time of the RCCB for different residual currents.
But RCCB breakers are designed to trip faster than must trip time needed for human safety.
Now figure 4 shows the actual tripping time of 30mA RCCB for different currents. These data are for a 30 mA trip rating type RCCB.

As per the chart, for a residual current of 15 mA current, the RCCB need not trip.
For a 30 mA current in the body or residual current in the RCCB, the RCCB will trip within a maximum of 300 mS.
The tripping time of a 30 mA RCCB is 300 mS maximum at a 30 mA leakage current, and the tripping time is 150 mS maximum at a 60 mA leakage current. So tripping time of the 30 mA type RCCB varies with the leakage or residual current. The tripping time of 30 mA RCCB will be less for higher residual current.
Then the same RCCB breaker with a residual current of 60 mA, will trip in 150 mS.
For a 150 mA current flows in the body or residual current in the RCCB, the RCCB will trip within a maximum of 40 mS.
The difference between the three current limits vs the tripping time of RCCB
Now I will explain the difference between three current vs time as above. I will take a 30 mA current flow in the body and a 30 mA type RCCB breaker as an example.
You will learn also the secret of the protection concept design now in the next para.
1st current – The body can take 30 mA for about 1 second (just approximately the time taken to explain) as per Fig 2.
2nd current – As the human body can take 30 mA for 1 second. Then the various standards say that we must trip RCCB earlier than 1 second to be safe. So standard says for a 30mA current, the RCCB must trip within 500 mS (approximately time) (Fig 3).
3rd current – Further, the manufacturer of the RCCB breaker design the RCCB, which will trip faster than the above must-trip time. For a 30 mA current, the must-trip time is 500 mS. Then RCCB is designed to trip faster, just in 300 mS. (Fig 4).
That is the reason “why 30 mA RCCB breaker is used”.
In brief – the tripping time for a 30 mA type RCCB breaker
If the current flows 30 mA in 30 mA type RCCB,
- The human body safety time limit is about 1 sec approximately
- Then the breaker must trip in less than 500 ms as per standard
- But actual RCCB will trip in less than 300 ms to be much safer
However, if the current is more than 30 mA, then RCCB will trip even faster as per figure 4.
For example, at 150 mA current in 30 mA type RCCB, it trips in about 40 mS.
Protection philosophy example
There are 3 levels always in a very simple type of protection philosophy (as in the above example). The 3 levels are explained with the above currents as an example.
- The body can take for a maximum of 1 sec time
- Must trip time is less than above, say 500 mS
- Actual protection operation is even faster, 300 mS in the above case
“So the actual setting of the electrical protective device is always lower than the must trip needed protection limit.
And must trip needed protection level is always lower than the boundary limit of the equipments need protection”
(G K Agrawal)
Where 30 mA RCCB breaker can not be used
Frequent tripping of the RCCB
Many times, 30 mA type RCCB trips very frequently, that too without humans touching it. It happens because of leakage current in some power equipment, generally in the industry.
So, 30 mA type RCCB is not practical to use in such cases. But still, we need to protect humans also.
Then, we follow the concept as per figure 5 to solve the above problem.
We use a 300 mA type of RCCB in place of the 30 mA type at the income. But this does not protect humans.
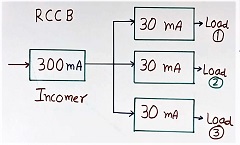
Then we divide all the loads into many branches. For example, loads are divided into 3 branches in the circuit as per Figure 5. Load 1, load 2, and load 3.
Then, we provide a 30 mA type RCCB breaker, one each in each branch as per Figure 5.
So there are three 30 mA type RCCB breakers, one for each load 1, load 2, and load 3. This will give protection to the human body also.
For example, suppose there is a big building having many flats. Then we can provide a 300 mA type RCCB at the incomer of the full building.
Further, we can provide a 30 mA type RCCB breaker for each flat.
Application of 30 mA type RCCB and 300 mA type RCCB
30 mA RCCB and 300 mA RCCB are used as follows:
- 30 mA type RCCB breaker finds use in human safety and home applications
- 300 mA type RCCB breaker finds application in the industry, commercial, and fire protection applications.
Where RCCB breaker does not protect
The RCCB breaker can protect if the current in the body flows into the earth. Refer to Figure 6. The human body is standing on earth (without rubber shoes) and touching a live wire.
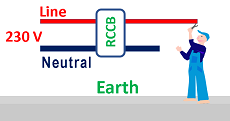
The RCCB breaker will provide protection in the above case.
Further, the RCCB breaker does not protect if the current in the body is not through the earth. Refer to figure 7. The human body touches the line and neutral wire both.
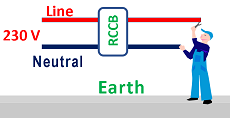
The RCCB breaker will not protect the human body in this case.
This kind of electrical shock is dangerous. Wearing rubber shoes also will not help.
Extra knowledge (of standard) – experience based
All of us, have limited knowledge (including myself). A time comes in the electrical or any equipment design field, that we do not know what to do.
In that case, I always refer to and read various related standards like IS and IEC, etc. These are technical documents written by technical experts from all over the world.
Further, these standards have such correct and proven information that it is mandatory to follow this all over the world many times.
In fact, when we make the specifications to buy some equipment (for the company), then we almost always include necessary IS standards reference also.
Further, many times, we insist that the manufacturer should test equipment as per IS standards in our presence.
I have learned a few things explained in this article by reading standards (in addition to theoretical documents and job experience).
To get more knowledge watch videos on youtube why 30 mA RCCB.
I hope that you enjoyed reading this post on the topic “Why 30 mA RCCB breaker is used in the home“
If so, then subscribe to my YouTube channel.
Read also What is AFCI breaker
Keep learning about the voltage of the neutral wire.
Further, read What is a potential transformer and its applications.
About the author – G K Agrawal B.Sc and B.Tech (from HBTU Kanpur), Retd. Sr DGM Design (BHEL), the inventor of patents, has lifelong industry experience in the electrical and electronics design field of R&D. He worked for BHEL. He shares his experience and knowledge on blogs and YouTube. Read the profile here.


1st time I read such an exellent information
Hi Sir,
Thanks for this excellent sharing. Keep it up!
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker / RCD -residual current device
ELR is Earth leakage Relay.
Just my opinion, because some might using the same term for both RCCB and ELR. The function almost the same but a bit different and RCCB is better.
For figure 7. ELR will not protect in the situation
but it mention RCCB which should protect in the situation.
Correct me if im wrong
Pingback: pills like tadalafil
Pingback: need help writing scholarship essay